JOKR: Joint Keypoint Representation for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Motion Retargeting
| Ron Mokady | Rotem Tzaban | Sagie Benaim | Amit Bermano | Daniel Cohen-Or |
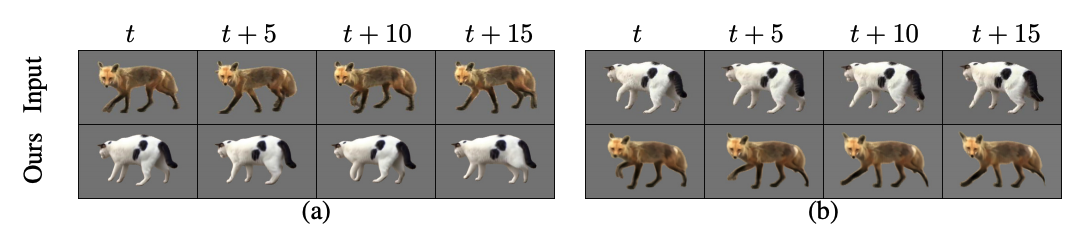 |
Motion retargeting results from a single video pair. The input videos (top) are used to generate the retargeting (bottom). As can be seen, each generated frame corresponds to the motion portrayed by the source, while keeping the style of the target. |
Abstract
The task of unsupervised motion retargeting in videos has seen substantial advancements through the use of deep neural networks. While early works concentrated on specific object priors such as a human face or body, recent work considered the unsupervised case. When the source and target videos, however, are of different shapes, current methods fail. To alleviate this problem, we introduce JOKR - a JOint Keypoint Representation that captures the motion common to both the source and target videos, without requiring any object prior or data collection. By employing a domain confusion term, we enforce the unsupervised keypoint representations of both videos to be indistinguishable. This encourages disentanglement between the parts of the motion that are common to the two domains, and their distinctive appearance and motion, enabling the generation of videos that capture the motion of the one while depicting the style of the other. To enable cases where the objects are of different proportions or orientations, we apply a learned affine transformation between the JOKRs. This augments the representation to be affine invariant, and in practice broadens the variety of possible retargeting pairs. This geometry-driven representation enables further intuitive control, such as temporal coherence and manual editing. Through comprehensive experimentation, we demonstrate the applicability of our method to different challenging cross-domain video pairs. We evaluate our method both qualitatively and quantitatively, and demonstrate that our method handles various cross-domain scenarios, such as different animals, different flowers, and humans. We also demonstrate superior temporal coherency and visual quality compared to state-of-the-art alternatives, through statistical metrics and a user study.
Cross-Domain Motion Retargeting
We demonstrate our results for the task of unsupervised cross-domain motion retargeting compared to other methods, for more details refer to the paper.
Paper
 |
[PDF] |
Code
 |
[Link] |
Other Results
We also show our method is valid for various domains.
Keypoints Interpretability
To demonstrate our meaningful keypoints representation, we present editing results obtained by moving a single or a pair of keypoints.
Temporal Regularization Ablation Study
The effect of omitting the temporal regularization is presented in the following video.
Last updated: June 2021